Lexicon
Flying Probe
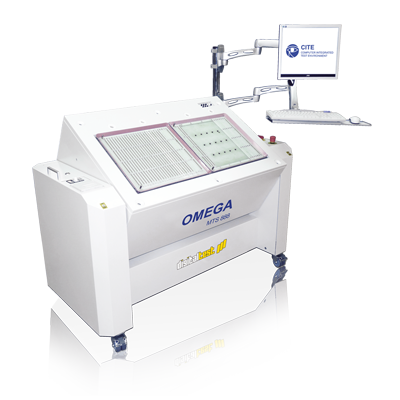
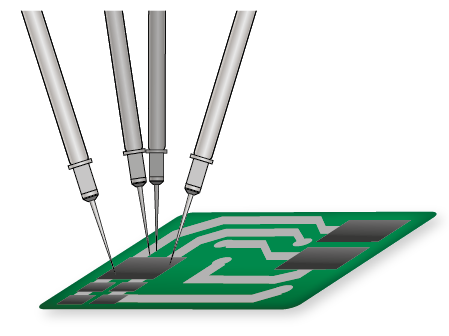
The Flying Probe Test (FPT) is an electrical test method which uses the in-circuit measuring method, and contacts the test object not via a bed of nails but via freely movable needles (probes). The needles are program-controlled and contact component pins or other contact points on a PCB in sequence.
Since the test points are scanned in sequence, this technology leads to longer test times, but enables the contacting of grid dimensions with pitches below 0.3 mm (Digitaltests Condor can even contact accurately on 0.1 mm pitches). At test point distances below 0.8 mm most fixtures can no longer complete testing. Another advantage of the flying probe test is fixtureless testing, which saves costs for fixtures and offers more flexibility. The test programs can be quickly and flexibly adapted to changing layouts.
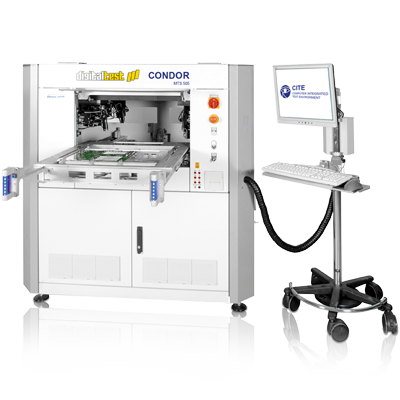
If the Flying Prober has several contact fingers/needles, four-wire measurements (greater measurement accuracy) can be carried out or several circuit nodes can be contacted simultaneously (higher test throughput).
Digitaltest's Flying Probe Tester Condor is equipped with a 4-head system and can optionally be supplemented with up to 1,012 fix Pins.